Socially Optimal Level Of Output
Section 01: Externalities
Adam Smith taught each individual, seeking but his own proceeds, "is led past an invisible hand to promote an cease which was no part of his intention," that finish beingness the public interest. Nevertheless, at that place are times when the market outcome differs from the outcome that society considers optimal. This market failure may occur when at that place is an externality, an external benefit or cost that is enjoyed or imposed on a third party other than the buyer or seller of the good. For example, consider your answer to the post-obit question:
What is the optimal level of pollution?
Most people would automatically requite the answer that naught pollution would be optimal. However, the optimal level of pollution is not nix; instead, the optimal level is obtained by following our economic determination rule of equating the marginal benefit to the marginal toll.
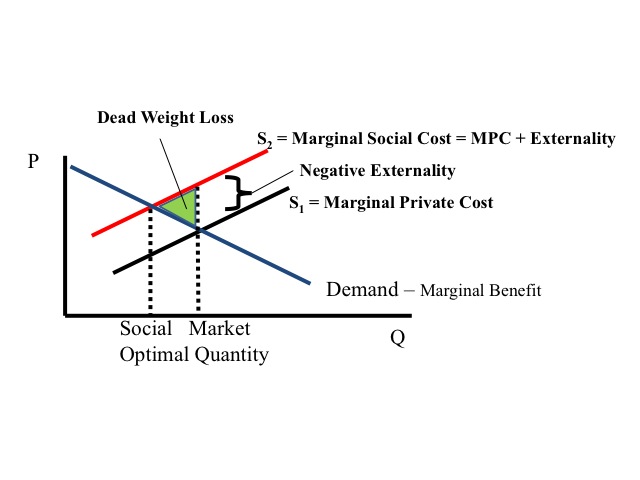
When a negative externality is present, in that location is a cost imposed on a tertiary party not involved in the production or consumption of the adept. Examples of negative externalities include various forms of pollution, such every bit air pollution from factories or ability plants, h2o pollution; noise pollution such as airports or even roommates; and drivers who are impeded past drugs, alcohol, or texting. Use the link beneath to view an ABC News twenty/20 video prune on noise pollution.
Click hither to watch the ABC News xx/20 video clip on "Too Much Noise."
If a factory is able to pollute without paying for the amercement caused past the pollution, it volition produce more than the socially optimal level of output. Since the business firm simply pays for the marginal private toll of producing the good or service, it will produce where the marginal private cost is equal to the marginal individual do good. Only when there are externalities, the marginal private price is not the aforementioned as the marginal social cost. The marginal social toll adds to the marginal individual cost the cost of the externality, which graphically is the vertical altitude between the marginal individual cost and marginal social price. If nosotros were to account for the negative externality, the optimal level of product would exist lower than the market quantity. Every bit is, the excessive quantity of output creates a deadweight loss to society since the marginal social cost exceeds the marginal social benefit.
Externalities may be in either the production or consumption of the good or service. Negative production externalities are generated when the skilful or service is produced such as factories polluting the air, water or land as they produce the practiced or service. Negative consumption externalities occur when the consumption of the expert or service creates the externality, for case an private that consumes alcohol at the bar and so, when driving home, kills pedestrians due to his impairment.
Property that is held in common, such as air, water, and public lands, belongs to everyone as a whole. Consequently no one individual has an incentive to care for it, since information technology doesn't belong to just her. In some higher apartments, dishes pile up in the sink or the garbage doesn't go taken out, considering it belongs to everyone collectively and no one individually. When a resource belongs to everyone, individuals account only for the private marginal benefits and costs and fail to account for the impact of their actions on others, hence the tragedy of the commons.
For case, if the ocean is mutual property there is a tendency to overfish because fishermen only consider their individual costs and do not account for how their larger catch makes it more costly for other fisherman to grab the fewer remaining fish. Similarly during the 19th century, American bison that once roamed much of North American were killed by the millions since they were a common resource. Because individuals actions fail to account for the touch on others, a negative externality exists.
Reference:
http://www.economicexpert.com/a/Tragedy:of:the:eatables.htm
http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/american-bison/
Positive Externalities
When a positive externality is present, the market place produces less than the socially optimal quantity of the good or service, since there is a benefit to society that is not captured by the individual. Educational activity, for instance, not only benefits the individual simply also society as a whole since individuals often are creating new products and services and are less probable to exist involved in trigger-happy crimes or on the welfare rolls of society. Yet, a pupil will only consider the marginal individual do good and the marginal individual cost when determining the quantity of education that he or she should obtain.
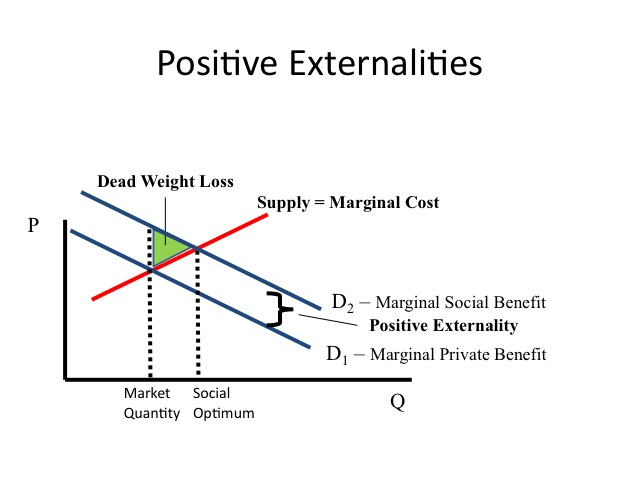
Other examples of positive externalities include immunizations or a neighbor who fixes up his firm which in turn increases the property value of other homes on the street. A deadweight loss also exists when there is a positive externality considering at the market quantity, the marginal social do good is greater than the marginal social price.
When an externality exists, the socially optimal output is not achieved. A multifariousness of different policies exist to correct these ranging from "control-and-command" to market-based policies.
Command-and-control options often include legislation limiting the amount of the activity along with regulatory bodies to monitor the behavior of the manufacture. For example, government may require all firms to cut emission levels past 30 pct within five years. Although these types of policies have been popular and care for all firms the same, they are likewise inefficient. For example, suppose there are two power plants producing pollution and each is required to cut emissions by 30 percentage and that i plant was very inefficient while the other had installed state-of-the-art technology and was already producing very trivial pollution. The marginal price of coming together the abatement goal is relatively depression for the inefficient firm but may exist extremely expensive for the plant that was already operating efficiently.
For common resources, such every bit fish and wildlife, government volition set harvest limits and issue a limited number of licenses that specify what tin can be caught and in what location. They may too restrict the equipment that can exist used in harvesting such every bit net or boat size. These laws not just set a given limit but are as well designed to increase the marginal individual cost. Fishing licenses, for instance, may set a maximum grab limit for the season but also set a daily grab limit.
Every bit limits are fix, the regime must monitor the behavior of firms to ensure that they are abiding by the standards. When a firm is out of compliance, fines are imposed. Since the probability of beingness caught out of compliance is non 100 per centum, these fines are oftentimes relatively loftier to discourage firms from taking the risk of existence out of compliance. If the fine is too depression, in that location is less incentive for firms to exist in compliance. For example, if the fine for possessing illegal recreational drugs is low behavior is not probable to modify. On the other hand, losing a limb or your life can serve as a strong deterrent for particular behavior.
For example a report institute that in Texas, excess pollution benefited firms past an estimated value of $8.6 million yet they were fined less than $ane.7 1000000. Consequently, firms may accept little reason to comply with the standards (http://www.redorbit.com/news/science/442700/report_says_texas_awash_in_overly_polluted_water/alphabetize.html).
With each police force, information technology is required that at that place be a penalisation associated with noncompliance. From two Nephi ii:13: "And if ye shall say there is no law, ye shall also say there is no sin. If ye shall say there is no sin, ye shall likewise say there is no righteousness. And if there be no righteousness there be no happiness. And if there be no righteousness nor happiness there be no penalty nor misery. And if these things are not there is no God. And if at that place is no God nosotros are not, neither the globe; for there could accept been no creation of things, neither to deed nor to be acted upon; wherefore all things must have vanished away."
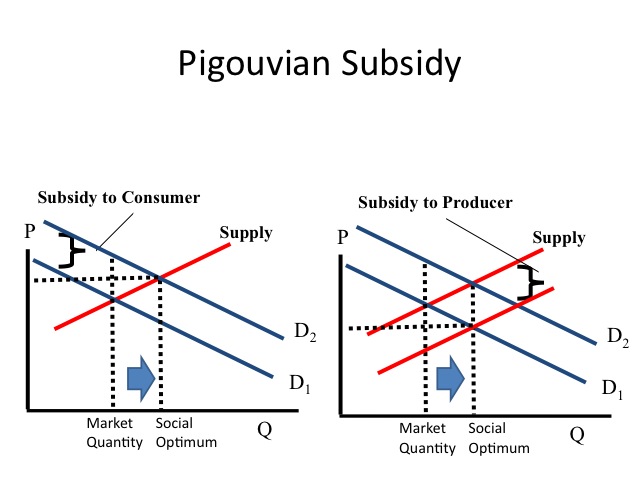
Economist Arthur Pigou recommended levying a tax on the proficient equal to the amount of the negative externality or a subsidy equal to the amount of the positive externality in order that firms internalize the externality.
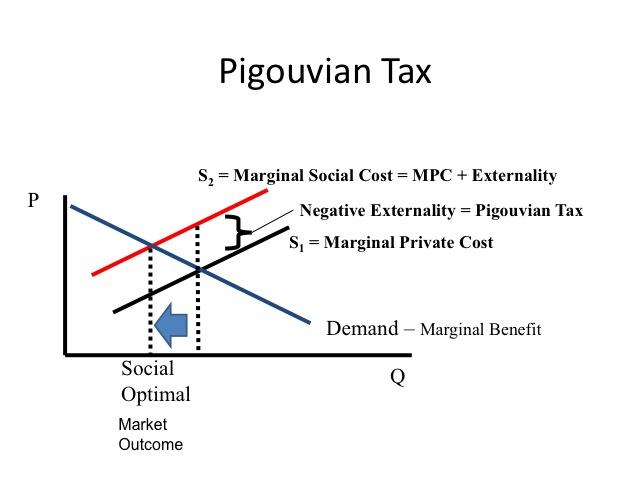
A firm producing a negative externality would pay its marginal private price plus a Pigouvian tax equal to the externality, and would thus reduce its production to the socially optimal level of output, since it would be paying for the impairment caused to others.
To right a positive externality, such as education, society can subsidized the consumer, increasing the demand for the practiced. Pell grants and other subsidized school loans increase consumer's demand for teaching. Alternatively, a subsidy may be given to the producer to reduce the marginal price of providing the skillful. States typically subsidize educational institutions allowing them to charge a tuition rate less than the marginal private cost. Another culling is for the regime to provide the good or service instead of the private market, for example, the majority of primary education (K-12) is provided by the government, with relatively piddling directly cost to the students.
Alternatively, government may decide the optimal level of pollution, then assign or sell tradeable emission permits, which permit firms to produce a sure amount of the item pollution, such as sulfur dioxide. The advantage of permits over the traditional command and control system, is that the pollution standard is met in a more efficient manner. To be in compliance, firms can purchase permits, install scrubbers or other devices that reduce the amount of pollution emitted, or reduce their output. Firms are able to meet the standards in the least cost method which benefits them as well as society. Since firms accept to buy permits to pollute, the externality is internalized and the socially optimal output level of the good is attained.
Reference for Sulfur Dioxide trading: http://www.ccfe.com/education_ccfe/SO2_Background_Drivers_Pricing_PDF.pdf
Coase Theorem
In 1991 economist Ronald Coase was awarded the Nobel Prize "for his discovery and description of the significance of transaction costs and holding rights for the institutional structure and functioning of the economy" (Nobel Prize Announcement). The Coase theorem argues that even when externalities exist, the efficient solution tin be reached as long as transaction costs, i.e., costs of negotiating , are low, property rights are assigned, and individuals are immune to negotiate. This efficient solution will be reached regardless of who is assigned the property right.
Permit's say that your roommate loves to barbecue merely it smokes upward the apartment and makes everything scent like smoke. If transaction costs were depression and your roommate was willing to negotiate, under the Coase theorem, how many nights would your roommate barbeque?
If y'all had the property right, you would prefer that your roommate not charcoal-broil at all, but given his passion for barbecuing, he'd exist willing to recoup you up to $10 if he could barbecue at least one night (existence the weekend). Based on the values in the table he would only have to pay y'all one dollar, to allow him the right to barbecue once a calendar week. His marginal value for the second and third nights are likewise greater than your marginal price. Thus with bounty, yous would let him to barbecue each of those nights. All the same for the fourth night, your marginal cost is greater than his marginal value, and so he would not be willing to pay you six dollars if it is only worth two dollars to him.
If your roommate had the property right, he would desire to charcoal-broil five nights a calendar week. You would be willing to pay him up to 8 dollars, if he reduced his barbecuing from v nights to iv nights. His marginal value of barbecuing the fifth night is only ane dollar, so he would be willing to give up that dark if he was compensated. Besides, his marginal value of quaternary dark is less than your marginal toll, so he would willing give up the quaternary night as well with compensation. Since your marginal cost is less than his marginal value for the third night, you would not be willing to pay for him non to charcoal-broil on the third night.
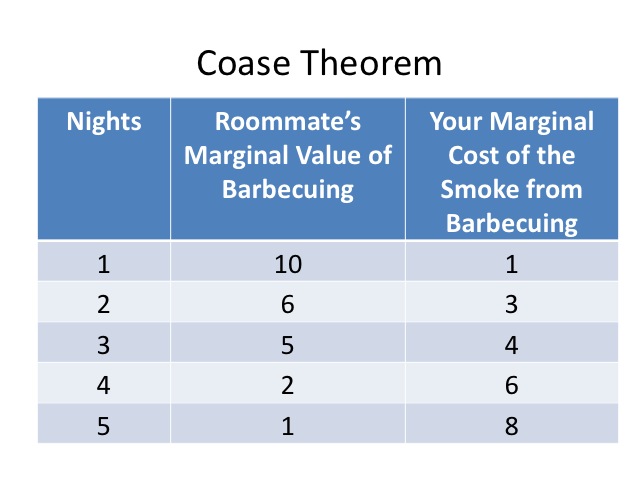
Every bit seen in our experiment, we reached 3 nights of barbecuing no matter who had the property right. While the efficient solution is reached under both scenarios, there is a difference in the income distribution.
In many cases, transaction costs are high and negotiating can exist difficult. Acid rain, for example, impacts a wide surface area involving millions of people. When belongings rights are non conspicuously defined, the matter is often taken to the judicial system. Some individuals will try to utilize the court system to force an result in their favor.
The importance of clearly defined belongings rights is discussed in the ABC News 20/20 video "Sharing is Improve."
Watch the ABC News 20/xx video "Sharing is Better."
Source:
http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1991/press.html
http://world wide web.marietta.edu/~delemeeg/games/games71-80.htm
Reference:
http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/bios/Coase
Private Goods / Public Good
All semester long, we take been talking about markets that involve private goods. Individual appurtenances are rival, excludable, and divisible. By "rival" we hateful that the consumption of the good or service by one prevents another from consuming the particular. Excludable ways that those who do not pay for the skilful or service, cannot consume it. Finally, individual goods are divisible meaning the production of the practiced or service can be divided among those who are consuming the skilful. For example if a firm produces 100 cars, each car tin can be divided and sold to a customer. To determine the market need for the good or service, we horizontally summed the demand curves of each of the individuals. For example, at five dollars one person would purchase 5 units and another would buy 2, and then the marketplace demand at five dollars would be vii units.
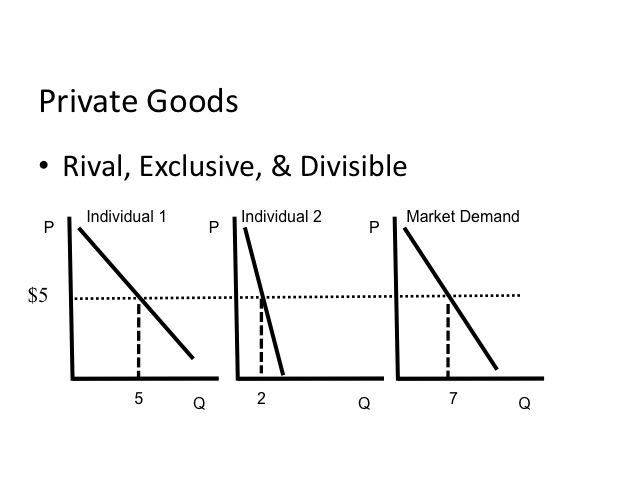
Equally we saw in our word of externalities, not all goods are private. Pure public goods are nonrival, nonexcludable, and nondivisible. National defense, for example, is a public good. The consumption, or in this example the protection, provided to ane person does not diminish the protection provided to another. Regardless of whether an individual living in the country paid for the service or not, he yet enjoys the benefits of that service. Last national defence force is non-divisible, pregnant nosotros can't separate upwardly the protection provided to each individual.
Being nonexcludable, in that location is a tendency for people to be free-riders, consuming the skilful without paying for it. Consider where many people sentry the fireworks on the 4th of July. While many stadiums often provide a testify within the stadium and charge an archway fee, well-nigh people watch the fireworks exterior the stadium, since once the fireworks are shot up into the air, they tin relish the fireworks without paying for them. Since people can savor the adept without paying for information technology, the private market produces less of the good or service than is socially optimal.
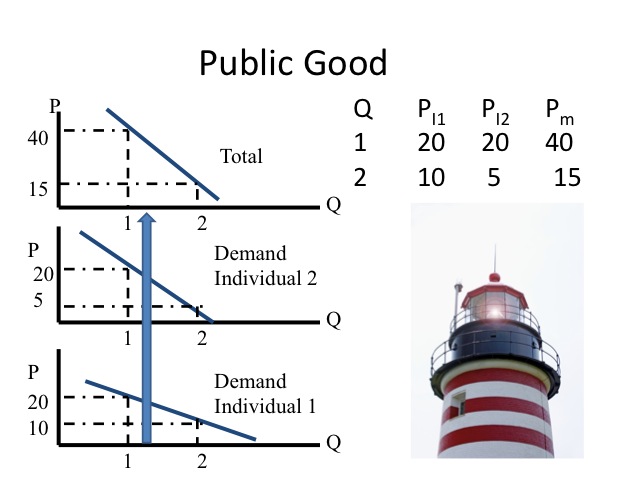
Being nonrival, more than 1 person can savour the expert. Thus to decide the socially optimal corporeality of the good or service, nosotros do a vertical summation of each individuals willingness to pay. For example, lighthouses tin provide service to more ane person and ane person's consumption does non diminish the consumption of some other. If two individuals in the market are both willing to pay 20 dollars to have a lighthouse, the willingness-to-pay for the kickoff lighthouse is $forty. For the second lighthouse, individual ane is only willing to pay 10 dollars and individual 2 is only willing to pay five dollars. Vertically summing each individual's willingness to pay, we tin derive the collective willingness to pay, similar in concept to the need curve. If the marginal cost of providing a lighthouse were thirty dollars, ane lighthouse would be socially optimal. Note that due to the costless-rider problem, no one private would be willing to provide a lighthouse, since the marginal cost exceeds her willingness to pay. To correct this market failure, government volition typically tax individuals and provide the good or service to the public.
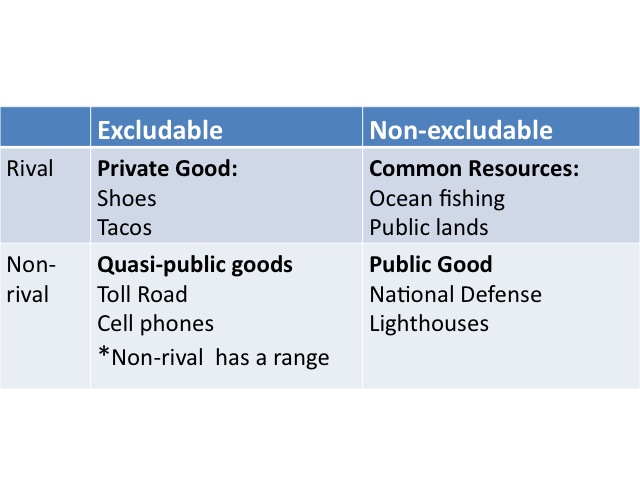
We take discussed two of the principal types of goods. Goods tin can be classified in one of four different categories: private, common resource, quasi-public goods, and public goods, based on whether the skilful is rival and excludable in the range of demand. Most appurtenances autumn into the category of private goods and considering they are excludable the market can provide the socially optimal quantity. Body of water fishing may be nonexcludable but rival, since the fish caught past ane tin not exist caught by another – information technology is a mutual resources good. A toll road firm is able to exclude those using the good, and at low levels of demand the roads are non-rival, meaning 1 person's use of the road does not diminish the enjoyment or use the road past some other – it is a quasi-public good. However, at high levels of utilize, such as during blitz 60 minutes roads exercise get rival since the enjoyment or use of the road by i is diminished by the use of others.
What is the M Canyon worth? If at that place was proposal to dam the Thousand Canyon and fill it with water to generate power for California, how much would yous be willing to pay to "save" the Chiliad Canyon? Alternatively, if this proposal was to get forward just the government wanted to compensate you for the loss of the Grand Canyon, how much would they have to pay yous? Equally you think of the answers to these 3 questions, you should inquire yourself if all iii of these answers might be the same? In many cases they volition differ since what an individual is willing to pay is bailiwick to his budget constraint and so he may have a low willingness to pay, yet he may consider the regime to accept no budget constraint so his willingness to accept is very large. This presents a claiming when determining the value of a public good, since we tin not look to the market place to see the current price for a Grand Coulee or some endangered species.
If individuals are concerned about the amount they will be taxed to provide or protect a skillful, their stated value may non reflect their truthful value. On the other hand, if individuals conceptualize a very loftier or depression stated value will laissez passer or reject a project just they won't have to pay their respective portion of the cost, they may give an unreasonable value while planning to be a free rider. Thus, the hypothetical value stated past individuals may not reflect their true value for the item.
In Nauvoo, when a member's house burned down, many of the men were talking proverb how pitiful they felt for the loss. Joseph Smith reached into his pocket and pulling out his money, and said, " I experience pitiful to the melody of five dollars'" and he gave it to the man. Willingly giving the human the money, reflects his actual willingness to pay.
Benefit/Toll analysis weighs the benefits of a project to the costs of a projection. Since benefits and costs may occur at unlike fourth dimension periods, we convert future values to a present value for a common comparison. To compute the present value of a time to come benefit or price, the futurity value is divided by (i+r)t, where r is the interest charge per unit expressed as a decimal and t is the number of years until the benefit or price is incurred. Consider the instance below.
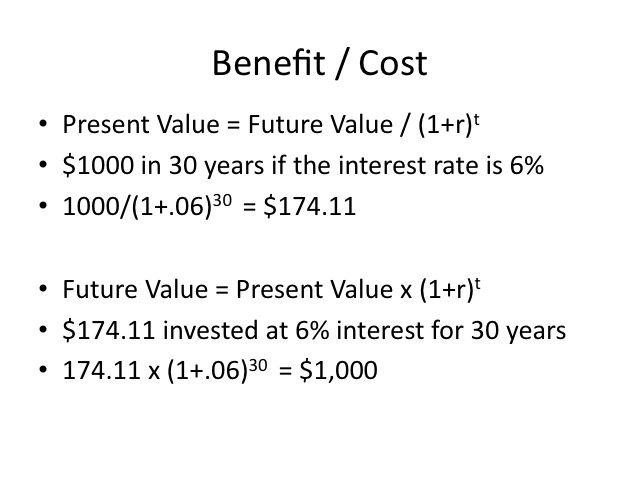
As seen in the example above, the present value of one,000 dollars received in xxx years if the interest rate is six pct would exist $174.11. Note that if the $174.eleven was invested at half-dozen per centum for 30 years, the future value would be 1,000 dollars.
Comparing the present value of the benefits to the nowadays value of the costs is useful in determining if it is worthwhile to undertake a project.
Another claiming associated with the provision of certain goods can be determining where to locate the detail. While individuals may be in favor of having the expert provided, such as an interstate, power constitute, or city dump, they don't wanted it located in their backyard.
Demand for power in some states has increased dramatically, yet state residents take resisted the development of new ability sources to meet the growing demands.
Watch the following video: http://www.youtube.com/picket?v=Mo2rMj8KVtQ&feature=related
Disproportionate Data
Disproportionate data can likewise create a market failure. Adverse choice can arise when information is known to one party in a transaction that is not known to the other, at the fourth dimension the contract is made. This is best illustrated with an example: when purchasing a used car, yous might consider which blazon of vehicle is most likely to be sold in the used motorcar market place, a "lemon" or a car that has performed well. Adverse selection would suggest that poor quality vehicles (adverse) are most likely. The seller may non disclose all he knows about the mechanical defects of the vehicle. Non knowing the honesty of the seller means, the price offered for the vehicle will probable be less to account for this risk. Similarly, those who need insurance the about are those most likely to purchase full coverage with low deductibles. Due to this take chances, insurance premiums are increased which causes some healthy individuals to decide not to buy coverage; this further increases the cost of the insurance and results in greater adverse selection.
Another asymmetric information problem is moral hazard. Moral hazard occurs when the behavior of one changes later on the contract is made. For example, those who purchase insurance may exist less inclined to have precautions after the purchase, knowing that they are insured. Or another example, lenders may see a big credit reserve left on a potential borrower'due south credit cards every bit a red flag. This may be the example, even if the borrower is a stellar customer and has never carried a residuum on the credit cards, considering of the potential that a large amount of credit could hands be obtained.
Sentinel: http://world wide web.pbs.org/newshour/video/share.html?southward=news01n14e0q123
A Charlotte, NC man turned in a fire insurance merits for a rare cigar collection, claiming "a series of modest fires." When the insurance visitor failed to pay, the homo sued and was awarded $15,000. However, after paying the merits, the insurance had the man arrested and charged with 24 counts of arson after he cashed the check. Land singer Brad Paisley summarize what happens in the song, The Cigar.
Reference: http://www.usaone.cyberspace/jokenet/jokes.asp?command=list&r=26
A variety of methods both individual and public tin can help to address these problems (all designed to get together information that the other political party knows).
one. Wellness insurance companies, for example, typically have individuals fill out a health history and complete a physical test to decide the premiums they will charge to the private.
2. Credit scores tin can also help companies appraise the likelihood of individuals repaying their loans and allow them to charge an appropriate interest rate. Those with good credit scores get amend rates, while those who have non managed their finances appropriately in the by are charged a college rate. Credit scores are also used in other areas, such equally auto insurance, since individuals who are irresponsible with their finances take a higher likelihood of being irresponsible in other behaviors likewise.
3. Deductibles are designed to foreclose the problem of moral take a chance. If individuals have to bear at least a portion of the price when they make an insurance claim, they are less likely to make a claim. Furthermore, the threat of having increased premiums or being dropped by the insurance company, tin can be a deterrent from moral hazard.
4. Product reports and reviews too provide data to help individuals make an informed determination. Publications such as Consumers Report are an contained review of products ranging from cars to washing machines. Movie reviews tin can exist benign to individuals trying to make an informed conclusion about the content of a picture and what to watch.
five. Consumers are as well more willing to purchase goods that offer warranties or money dorsum guarantees. Many consumers often have the perception that products with good warranties are amend. While this is not necessarily the case, it reduces the risk associated with purchasing the proficient. Even though a production may offering a warranty, there is a cost associated with returning the lacking product and keeping the necessary paperwork to have the business firm honor the warranty.
6. Franchises are another manner firms utilize to accost disproportionate information. Restaurant chains, for example, strive to have a relatively consistent product at each location. Thus if y'all are visiting a new metropolis, you know what to expect if you become to a national restaurant chain.
Authorities is also involved in addressing the problems of disproportionate information.
1. Government has set diverse standards to insure a minimum quality ranging from food products, such as class A milk, to bar exams to insure that individuals practicing constabulary have some minimum competency. Some professions crave that individuals receive additional preparation in their corresponding profession annually to maintain their license.
2. Inspections also promote confidence in what is being purchased. For case when filling your car up with gas, we trust that we are receiving non only the quality only also the quantity of what is indicated on the pump, because the Section of Weights and Measures has indicated that the pump has been checked and approved.
3. Various laws restrict certain activities such as insider trading. Individuals inside a company are restricted from selling their stock due to information they know nigh the visitor, prior to the data existence released publically.
4. The government also may also publish reports disclosing specific information about an manufacture, such as accident and death rates. This allows individuals considering an industry to know more of the potential risks of the industry. In addition, agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Assistants (OSHA) require businesses to provide certain working conditions and impose fines when the firms are not in compliance.
While government plays a role in correcting sure market failures, they may not solve the trouble for several reasons:
1. Principal-agent trouble. For example, if a person in accuse of the nation's welfare plan (the agent) does such a swell job he gets anybody off welfare (equally desired by the citizens – the principals), he no longer has a job. Thus, he has the incentive to grow the welfare program so his position is more of import with a larger upkeep. If the goal of a pol is to go reelected, he may pursue policies that are politically popular just impose additional costs on society at some later time catamenia. The growing national debt, is testify, that politicians would rather spend today and forcefulness some futurity generation to pay for it.
2. Government may neglect to recognize and account for the unintended consequences of their actions. Earlier nosotros mentioned, overflowing insurance that was designed to provide affordable insurance to those in overflowing prone areas. However, the subsidized insurance has atomic number 82 to additional people building in areas that are flood decumbent, due to the government subsidy. Another example is home ownership, which is politically pop; yet, a portion of the housing crunch can exist traced back to authorities "encouraging" banks to lower their lending standards and result mortgages to individuals who would non otherwise be considered credit worthy.
Watch http://www.youtube.com/scout?v=uBVMni4B4us
iii. Given the bureaucratic nature of government, regime intervention generally takes longer and costs more than originally predictable. More intervention leads to more laws and more administrative bodies to enforce those laws, which adds boosted costs to the tax payers. Furthermore, many of the issues regime addresses are large and complex in nature with many unknown factors, making information technology difficult to pass a meaningful effective neb that focuses on the trouble.
iv. Regulatory Capture is another potential regime failure when the regulatory agency acts in the involvement of those information technology is assigned to regulate. As described by the Economists magazine:
"The theory of regulatory capture was ready out by Richard Posner, an economist and lawyer at the Academy of Chicago, who argued that 'Regulation is non about the public involvement at all, but is a process, by which interest groups seek to promote their private interest ... Over time, regulatory agencies come to be dominated by the industries regulated.' Most economists are less farthermost, arguing that regulation often does good but is always at risk of existence captured by the regulated firms."
(http://www.economist.com/research/Economics/alphabetic.cfm?letter of the alphabet=R).
On the other hand, those with more extreme views of regulation may pursue office or positions in government in club to pass legislation aligned with their views, which may not be in the involvement of society equally a whole.
Given theses challenges, regime should weigh the benefits of market intervention relative to the costs to determine if society would be improve off or worse off with the government involvement. As citizens it is incumbent upon u.s. to elect wise authorities officials who will uphold the Constitution and institute righteous laws, in additional to existence willing to be personally involved (D&C 98:x). The Volume of Mormon is replete with examples of nations prospering when righteous leaders were elected and stumbling when wicked leaders were in office.
In 1998, the First Presidency stated:
"We wish to reiterate the divine counsel that members 'should be anxiously engaged in a good crusade, and do many things of their own free will, and bring to pass much righteousness' (D&C 58:27) while using gospel principles every bit a guide and while cooperating with other like-minded individuals.
"Through such wise participation as citizens, we are then in better compliance with this scripture: 'Governments were instituted of God for the benefit of man; and … he holds men accountable for their acts in relation to them' (D&C 134:one).
"Therefore, as in the by, we urge members of the Church building to be full participants in political, governmental, and community affairs. Members of the Church are nether special obligations to seek out and then uphold those leaders who are wise, good, and honest (meet D&C 98:10).
"Thus, we strongly urge men and women to be willing to serve on school boards, city and county councils and commissions, state legislatures, and other high offices of either election or appointment, including involvement in the party of their choice.
Reference: "First Presidency Urges Citizen Participation," Ensign, April. 1998, 77
Socially Optimal Level Of Output,
Source: https://courses.byui.edu/econ_150/econ_150_old_site/lesson_11.htm
Posted by: goodehounce.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Socially Optimal Level Of Output"
Post a Comment